Common Cybersecurity Threats
 Phishing
Phishing
Phishing is a cyberattack where attackers disguise themselves as a trustworthy entity, like a bank or a popular online service, in emails, text messages, or instant messages. The goal is to trick you into revealing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details.
These fraudulent messages often lead to a fake website that looks identical to the real one. If you enter your credentials on the fake site, the attacker captures them.
Signs to Watch For:
- A Sense of Urgency: Messages that threaten to close your account or demand immediate action are classic red flags.
- Suspicious Links or Attachments: Hover over links before you click to see the actual URL. Be wary of unexpected attachments, even if they seem to be from someone you know.
- Poor Grammar and Spelling: Legitimate companies usually have professional editors. Obvious mistakes can indicate a scam.
- Generic Greetings: A message that uses "Dear Customer" instead of your actual name is suspicious.
- Mismatched Sender Address: The sender's email address might look legitimate at a glance, but upon closer inspection, it may be a slightly altered or completely different domain.
 Malware
Malware
Malware, short for "malicious software," is a general term for any intrusive software developed by cybercriminals to steal data and damage or destroy computers and computer systems. It can get onto your device without your knowledge and can include viruses, spyware, ransomware, and more.
Common Types of Malware:
Ransomware
This type of malware encrypts your files or locks you out of your entire device. The attackers then demand a ransom (usually in cryptocurrency) in exchange for the decryption key to restore your access.
Spyware
Spyware secretly installs itself on your computer to collect information about you, your browsing habits, and your sensitive data (like login credentials and credit card numbers) without your consent.
Trojans
A Trojan (or Trojan Horse) disguises itself as a legitimate file or program. Once you download and run it, the Trojan activates, creating a backdoor that allows other malware to be installed or gives attackers direct access to your system.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Keep Software Updated: Always install the latest security updates for your operating system and applications.
- Use Antivirus Software: Install reputable antivirus/antimalware software and keep it running and updated.
- Be Cautious with Downloads: Only download software from official websites and app stores. Be wary of free downloads from untrusted sources.
- Don't Click Suspicious Links: Avoid clicking on links in unsolicited emails or messages, as they can lead to malicious downloads.
 DoS/DDoS Attacks
DoS/DDoS Attacks
A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack aims to make a website or online service unavailable to its intended users. The attacker does this by flooding the target server with so much traffic that it becomes overwhelmed and either slows down to a crawl or crashes completely.
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack is a larger-scale version of a DoS attack. Instead of using one source, the attacker uses a network of compromised computers (often called a "botnet") to send the flood of traffic from many different sources at once, making it much harder to stop.
For a regular user, the main effect of a DoS/DDoS attack is the temporary inability to access a favorite website, game, or online service.
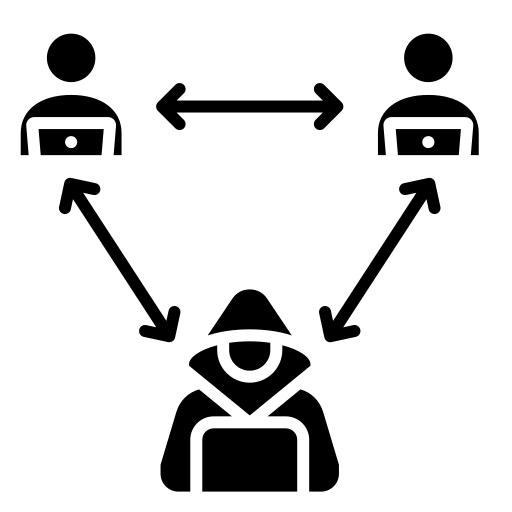 Man in the Middle (MitM) Attacks
Man in the Middle (MitM) Attacks
A Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack is when an attacker secretly intercepts and relays communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other. This allows the attacker to eavesdrop on the conversation, steal data, and even alter the messages being sent.
These attacks are common on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks.
 Social Engineering
Social Engineering
Social engineering is the art of psychologically manipulating people into performing actions or divulging confidential information. Unlike other threats that might exploit software vulnerabilities, social engineering exploits human trust and curiosity. It's often the first step in a larger attack. Phishing is a very common form of social engineering.
Common Techniques:
Pretexting
This is when an attacker invents a scenario (a pretext) to gain your trust and convince you to provide information. For example, they might impersonate a co-worker, IT support, or a bank official to ask for a password or other sensitive data, claiming they need it for a legitimate reason.
Baiting
Baiting uses a false promise to pique a victim's greed or curiosity. The attacker might leave a malware-infected USB drive in a public place labeled "Confidential Salaries" or offer a free movie download online. When the victim takes the "bait," their device becomes infected.
 Welcome to CyberSafe
Welcome to CyberSafe